What is a GPU in a computer and a troubleshooting guide for high GPU usage by the desktop window manager
Jul. 09, 2025 / Updated by Seraphina to Windows 10

GPU stands for Graphics Processing Unit in a computer. It is a specialized processor unit responsible for handling graphics and image data, accelerating graphic rendering, and processing tasks. GPUs are commonly used in applications such as computer gaming, video editing, 3D modeling, and data visualization, which require extensive graphic computations. Compared to CPUs, GPUs excel in parallel processing capability and graphic processing, providing faster graphic rendering speeds and smoother graphic performance.
Contents:
3. Choosing a GPU for Your Computer
4. Troubleshooting Guide for High GPU Usage by Desktop Window Manager
NVIDIA GPU cards are graphics acceleration cards integrated with Graphics Processing Units produced by NVIDIA Corporation. These cards are used to provide performance in computer graphics processing, including gaming, graphic design, video editing, and other fields. The performance of NVIDIA GPU cards depends on factors such as their core architecture, memory capacity, and frequency.
NVIDIA GPU cards are widely used in the PC gaming and workstation fields. The product series include GeForce, Quadro, and Tesla. The GeForce series mainly targets the consumer market, providing high-performance graphic processing solutions for gaming enthusiasts; the Quadro series focuses on professional graphic design, video editing, and engineering applications, providing more stable and optimized performance; while the Tesla series is aimed at high-performance computing and scientific computing markets, used for tasks such as deep learning, artificial intelligence, and large-scale data analysis.
The technology of NVIDIA GPU cards is continuously updated, with new cards typically having higher performance, lower power consumption, and more advanced features to meet the growing computational demands.

Performance: Including graphic processing performance, computational performance, rendering speed, etc. Performance testing can be evaluated through various benchmark tests and actual applications.
Memory Capacity and Bandwidth: Memory capacity and bandwidth are crucial for handling large graphic data and high-resolution images. Larger memory capacity and higher bandwidth can improve performance and processing speed.
Power Consumption: Low-power design can bring higher energy efficiency and less heat dissipation requirements, which are crucial for energy-saving and heat management.
Price: The price of GPU cards is usually a key factor in purchasing decisions. GPU cards from different brands and models may have significant differences in price, so it's necessary to balance between performance and budget.
Supported Features: Including supported graphic APIs (such as DirectX, OpenGL, Vulkan), hardware acceleration features (such as ray tracing, DLSS), multi-monitor support, video encoding, etc.
Brand and Technical Support: GPU cards from different brands may provide different levels of after-sales support, driver updates, and technical support. Brand reputation and user experience are also considerations.
Heat Dissipation and Design: Heat dissipation solutions and designs of GPU cards are crucial for performance stability and noise levels. Some high-end GPU cards may be equipped with advanced heat sinks and fan designs to provide better heat dissipation performance and lower noise.

Application Scenarios: It's essential to choose the appropriate GPU card based on user needs and usage scenarios. For example, gamers may focus more on graphic performance and frame rates, while professional designers may focus more on color accuracy and workflow optimization.
3. Choosing a GPU for Your Computer:
Performance: Look for a GPU that meets your performance requirements, whether for gaming, content creation, or professional applications. Consider factors such as clock speed, CUDA cores (for NVIDIA GPUs), and memory bandwidth.
Compatibility: Ensure that the GPU is compatible with your computer's motherboard and power supply. Check the GPU's PCIe slot version and power requirements to ensure compatibility.
Memory: Consider the amount of VRAM (Video Random Access Memory) provided by the GPU, as it affects performance and the ability to handle high-resolution textures and large datasets.
Heat Dissipation: Look for GPUs with efficient heat dissipation solutions to ensure performance and longevity. Optional heat dissipation methods include fan-based air cooling or liquid cooling solutions.
Value for Money: Compare the price and performance of GPUs to determine their value for money. Sometimes, mid-range GPUs offer better value for money than high-end models.
Brand and Support: Consider the reputation of GPU manufacturers and their customer support and warranty policies. Well-known brands like NVIDIA and AMD typically offer reliable products and good support.
Connectivity: Check the ports and connection options of the GPU to ensure compatibility with your monitor and other peripherals. Look for DisplayPort, HDMI, and DVI ports based on your monitor inputs.
Future Expansion: Consider the compatibility of GPUs with future upgrades and upcoming technologies. Look for GPUs that support features like DirectX 12 Ultimate, ray tracing, and DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling) to ensure future scalability.
Reviews and Recommendations: Read reviews and user feedback to understand actual performance and reliability. Websites and forums dedicated to discussing PC hardware are valuable resources for gathering information and recommendations.
Personal Preferences: Consider any personal preferences you may have, such as brand loyalty, aesthetics, or specific features that are important to you.
4. Troubleshooting Guide for High GPU Usage by Desktop Window Manager:
1). Update Graphics Card Drivers:
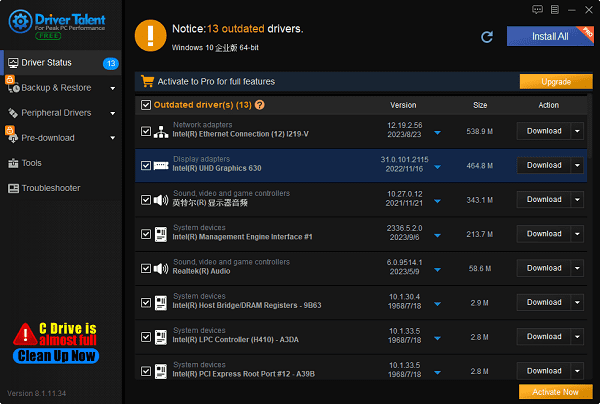
Ensure that your graphics card drivers are up to date. You can use software like "Driver Talent" to detect and update your computer's drivers with a single click. If the detection results show that an update is needed, click the "Download" button to download and install the driver, then restart your computer to ensure that the new driver is working properly. Alternatively, you can also visit the official websites of graphics card manufacturers such as NVIDIA, AMD, or Intel to download and install the latest drivers.
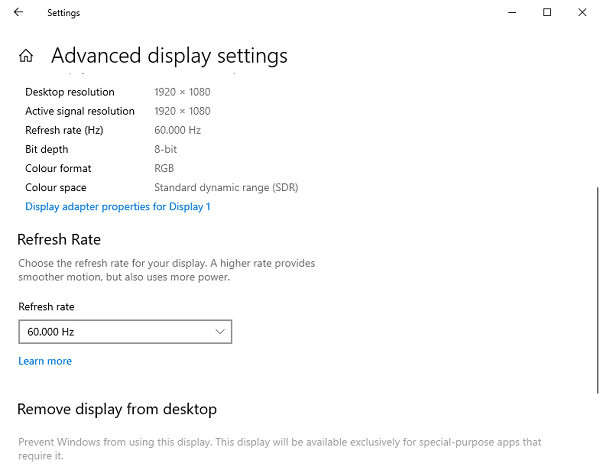
2). Lower Display Settings:
Try lowering display settings such as resolution, refresh rate, and display effects to reduce the GPU load.
3). Disable Visual Effects:
In the Windows operating system, you can disable some visual effects to reduce the GPU load. Right-click on "This PC" (or "My Computer"), select "Properties" > "Advanced system settings" > "Performance settings," then choose "Best performance".
4). Close Unnecessary Programs:
Close background programs that are not needed, especially those that may consume GPU resources. Use Task Manager (Ctrl + Shift + Esc) to see which programs are using a significant amount of GPU resources and try closing them.
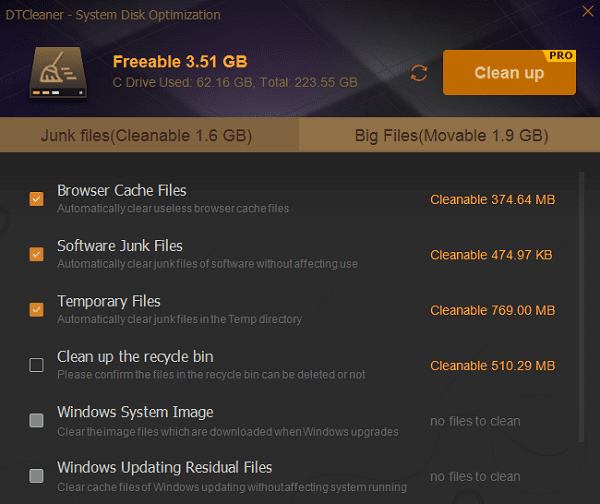
5). Clean System Junk:
Regularly clean system junk and temporary files to maintain system performance. You can use system cleaning tools or the DTCleaner software in Driver Talent to accomplish this task.
6). Check Hardware Cooling:
Ensure that your computer's cooling system is working properly to prevent GPU overheating. Clean the computer's fans and heat sinks to ensure proper airflow.
7). Adjust Power Options:
In Windows, you can reduce GPU power consumption by changing power options. Open "Control Panel" > "Power Options", select "Change plan settings", then adjust advanced power settings in the high-performance plan to reduce GPU power consumption.
8). Check for System Viruses:
Run antivirus software to scan your computer for possible malware or viruses. Sometimes, malware may cause high GPU usage.
Above is the explanation of what a GPU is in a computer and a troubleshooting guide for high GPU usage by the desktop window manager. If you encounter driver-related issues such as network cards, graphics cards, Bluetooth, sound cards, etc., you can download "Driver Talent" for detection and repair. "Driver Talent" supports driver download, installation, backup, and other functions, providing flexible driver management.
See also:
Is it essential to update computer drivers
Steps to clean up a full C drive on the computer
How to Solve the Issue of Keyboard Lights Not Turning On
No Internet Connection-5 Common Solutions
How to Solve Slow Speed and High Latency on Win11 Computers

|
ExplorerMax |

|
Driver Talent for Network Card | |
| Smart and advanced file explorer tool for Windows platforms | Download & Install Network Drivers without Internet Connection | |||
| 30-day Free Trial | Free Download |







