What does a wireless USB do and tutorial for using USB wireless network card
May. 06, 2024 / Updated by Seraphina to Windows 10

Wireless USB adapters are portable devices typically inserted into a computer's USB port to enable wireless network connections. They facilitate connectivity by receiving and transmitting Wi-Fi signals, allowing computers, laptops, or other devices to connect to Wi-Fi networks even if they lack built-in wireless functionality. Wireless USB adapters can be used for internet access, LAN connections, gaming, streaming, multimedia transmission, and more, providing users with a convenient wireless connectivity solution.
CONTENTS:
1. Composition of Wireless USB Adapters
4. Instructions for Using USB Wireless Adapters
1. Composition of Wireless USB Adapters:
USB Interface: The USB interface connects the adapter to the computer or other devices for data transmission and power reception. It usually adopts a standard USB Type-A interface, compatible with most computers and devices.
Antenna: Wireless USB adapters typically come with one or more antennas for receiving and transmitting wireless signals. The design and quantity of antennas affect the adapter's signal reception quality and transmission distance.
RF Chip: The RF chip is a key component of wireless USB adapters, responsible for handling the transmission and reception of wireless signals. It's usually connected to the antennas and communicates with wireless networks via radio frequency signals.
Circuit Board: Various electronic components, including the RF chip, antenna connectors, and USB interface, are integrated into the circuit board to ensure the adapter's normal functionality.
Casing: The casing serves as the external shell protecting the internal circuits and components of the adapter. Typically made of plastic or metal, it offers durability and heat dissipation.
1). Definition:
A wireless USB hub extends a single USB port into multiple wireless-connected ports. It utilizes Wi-Fi technology to enable multiple devices to wirelessly connect to a computer or other host without directly connecting to physical USB ports. Wireless USB hubs are commonly used to expand device connectivity range, allowing users to conveniently share files, print documents, connect external storage devices, etc., without the limitations of wired connections.
2). Composition:
Base Station (Hub): This core component of the wireless USB hub communicates with the computer and manages connections with external devices. It typically features multiple USB ports for connecting to the computer and external devices.
Wireless Transceiver: A critical component within the base station, the wireless transceiver establishes wireless communication with the computer. It receives data from the computer and transmits it to external devices connected to the USB hub, and vice versa.
External Devices: These are various USB devices connected to the wireless USB hub, such as printers, cameras, keyboards, mice, and storage devices. They connect to the USB hub via USB ports and communicate data through the base station.
Power Adapter: Wireless USB hubs typically require power to support connected external devices. The power adapter supplies power to the hub, ensuring its normal operation.
1). Definition:
A USB wireless extender extends the range of USB connections wirelessly using Wi-Fi technology. It allows users to establish wireless connections between devices and computers without the use of long cables or being restricted by wired connections. USB wireless extenders typically consist of a base station and one or more wireless receivers. The base station connects to the computer's USB port, while the receiver connects to external devices such as printers, cameras, or storage devices. This device simplifies device setup, reduces cable clutter, and provides greater flexibility and convenience.
2). Composition:
Transmitter: This core component of the USB wireless extender converts USB signals into wireless signals and transmits them to receivers. It typically connects to the computer or USB devices and transmits signals wirelessly.
Receiver: Another key component, the receiver, receives wireless signals from the transmitter and converts them back into USB signals. The receiver is usually connected to USB devices located remotely, enabling them to communicate wirelessly with the computer.
Antenna: Antennas facilitate wireless signal transmission between the transmitter and receiver, ensuring stable connection quality and extended transmission distance.
Power Adapter: USB wireless extenders typically require power to support signal transmission. The power adapter supplies power to both the transmitter and receiver, ensuring their proper operation.
4. Instructions for Using USB Wireless Adapters:
1). Preparation for Installing USB Wireless Adapters:
A USB wireless adapter
Driver software CD or downloaded drivers from the manufacturer's website
A computer requiring wireless network connection
2). Installing Driver Software:
Insert the USB wireless adapter into the computer's USB port.
If the computer does not automatically recognize the adapter and install the driver software, you can use "Driver Talent" software for one-click detection and automatic installation. The software can automatically match the corresponding driver without needing to know the adapter's model or brand. Simply click to download.
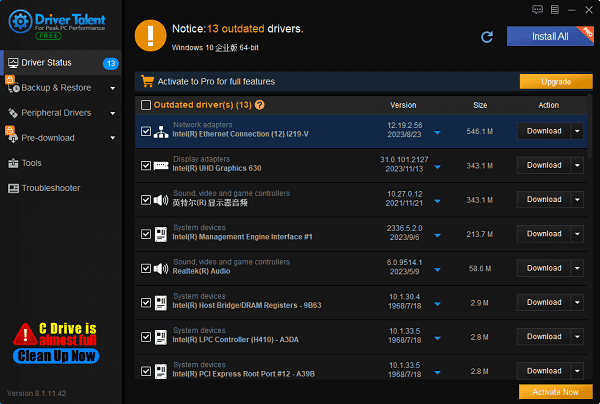
During the installation process, you may need to restart the computer, so follow the prompts accordingly.
3). Connecting to a Wireless Network:
After the driver software installation is complete, you will see a wireless network icon in the taskbar notification area of your computer.
Click the icon to display the available wireless network list.
Select the network you want to connect to and click "Connect". If the network is encrypted, you'll need to enter a password.
Once connected successfully, you can start using the wireless network.

4). Configuring Network Settings:
If you need to configure specific network settings such as a static IP address or DNS server, you can do so by:
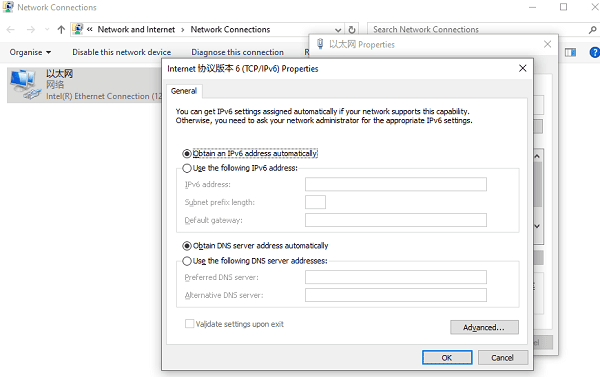
Opening "Control Panel" and finding "Network and Sharing Center".
Clicking "Change adapter settings", right-clicking on the wireless network connection, and selecting "Properties".
In the "Networking" tab, you can set IP addresses, DNS servers, etc.
5). Troubleshooting Wireless Adapters:
If you encounter problems during use, you can try the following methods:
Ensure the USB wireless adapter is securely inserted into the USB port.
Restart the computer; sometimes this can resolve temporary connection issues.
Check the wireless network signal strength to ensure you're not in a weak signal area.
These are the uses of wireless USB and instructions for using USB wireless adapters. If you encounter driver-related issues with network cards, graphics cards, Bluetooth, sound cards, etc., you can download "Driver Talent" for detection and repair. Additionally, Driver Talent supports driver downloads, installations, backups, etc., providing flexible driver management.
See also:
AMD Releases New Driver: Version 24.4.1 for Comprehensive Upgrade Experience
Fix: Dell computer displays English letters during startup and fails to boot
What does broadband mean and a troubleshooting guide for resolving broadband connection error 651
What is a HDMI used for and the solution to no sound on an external monitor connected via HDMI

|
ExplorerMax |

|
Driver Talent for Network Card | |
| Smart and advanced file explorer tool for Windows platforms | Download & Install Network Drivers without Internet Connection | |||
| 30-day Free Trial | Free Download |








