Choosing the right CPU is crucial when building or upgrading a PC. This article compares Intel and AMD based on performance, use cases, pricing, and ecosystems to help you decide.
1. Key Features of Intel and AMD CPUs
1). Intel's Advantages
Single-Core Performance:Intel processors are renowned for their excellent single-core performance, ideal for high-frequency applications like gaming and some professional software.
Stability and Compatibility: Intel CPUs offer reliable hardware and software compatibility, with well-optimized drivers.
Power Efficiency and Heat Management: Especially in the 13th-gen Core series (e.g., i5-13600K, i7-13700K), Intel excels in managing power and heat, making them suitable for prolonged use.
2). AMD's Advantages
Multi-Core and Multi-Threaded Performance: AMD Ryzen CPUs, with more cores and threads, shine in multitasking and rendering workloads.
Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to similar Intel models, AMD Ryzen CPUs, especially the Ryzen 5 and Ryzen 7 series, often deliver better value.
Support for Latest Technologies: AMD leads in adopting cutting-edge technologies like PCIe 4.0/5.0 and DDR5 memory.
2. Maximizing CPU Performance
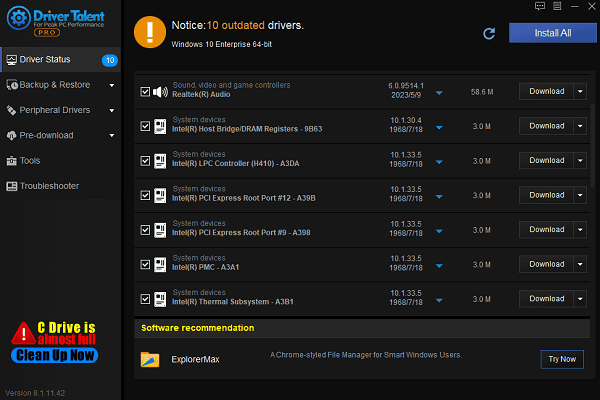
Whether you choose Intel or AMD, both CPUs require proper driver installation and occasional updates to optimize communication with the operating system. Using Driver Talent can simplify this process, ensuring you avoid the risks of downloading incorrect drivers while saving time.
Download and install the latest version of Driver Talent. Open the software and click "Scan".
After scanning, identify outdated or missing drivers from the list. Locate the CPU driver and click "Download".
Restart your computer after updating to ensure the new driver functions correctly.
3. Key Factors in Choosing a CPU
1). Use Case Determines Choice
Gamers: Intel's high frequency and stable performance excel in many AAA games. The Core i5 and i7 series are great for high-frame-rate gaming. AMD Ryzen CPUs, with their multi-core capabilities, are better suited for resource-intensive games optimized for multi-threading.
Content Creators: For video editing, 3D rendering, or audio production, AMD Ryzen CPUs with superior multi-core processing, such as the Ryzen 9 series, are ideal.
Office and Everyday Use: Basic tasks like browsing or office work require less CPU power. Intel's Core i3 or AMD's Ryzen 3 series are sufficient.
2). Budget Planning
If you're on a tight budget, AMD typically offers similar performance at a lower price. In the mid-range segment, the Ryzen 5 and Ryzen 7 series are more cost-effective than comparable Intel products.

3). Power Consumption and Heat
High-performance CPUs from both brands generate significant power and heat under load. However, AMD's Ryzen 5000 series and newer models are more energy-efficient, ideal for users prioritizing lower temperatures and energy savings.
4). Motherboard Compatibility
Intel CPUs require specific chipsets (e.g., Z790, B760) and may necessitate motherboard upgrades.
AMD, with its long-term support for AM4 and AM5 sockets, allows users to upgrade CPUs without frequently replacing motherboards.
4. Popular CPU Comparisons
| Model | Cores/Threads | Base Frequency (GHz) | Use Case | Price (USD) |
| Intel Core i5-13600K | 14/20 | 3.5 (Turbo 5.1) | Gaming, Office | ~$320 |
| AMD Ryzen 5 7600X | 6/12 | 4.7 (Turbo 5.3) | Gaming, Light Creation | ~$299 |
| Intel Core i7-13700K | 16/24 | 3.4 (Turbo 5.4) | Gaming, Multitasking | ~$420 |
| AMD Ryzen 9 7950X | 16/32 | 4.5 (Turbo 5.7) | Professional Creation | ~$700 |
Intel is best for high-frequency and stable performance, while AMD offers better multi-core efficiency and value. Choose a CPU compatible with your motherboard, memory, and power supply for optimal results.
See also:
6 Ways to Resolve LogiLDA.dll Missing on Windows
Ways to Fix ntdll.dll Crash Error on Windows
Ways to Fix Windows 10 Not Detecting WiFi Error









